FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: Date June 14, 2021
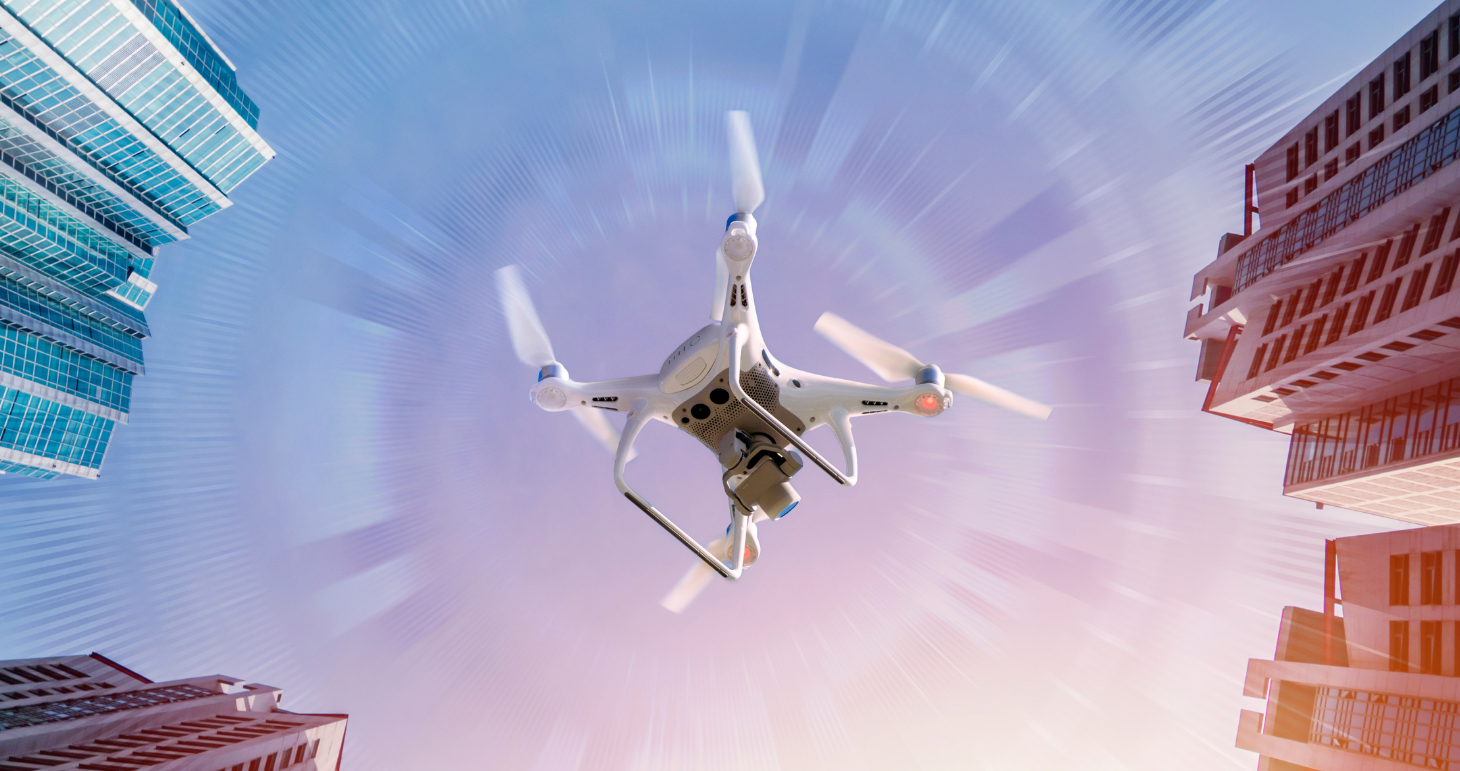
Hilliard, Ohio – GhostWave Inc.’s integrated optical-radar sensor fusion system, which brings awareness of other objects in and within the vicinity of a drone’s flight path, comes at an important time. On April 21, 2021, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) announced its new remote identification rules and provisions that are intended to minimize risks to other aircraft, people, and property on the ground. Now, more than ever, drone safety has become a central topic as drone use becomes more widespread and their integration into the national airspace expands.
According to the FAA, the rule on remote ID requires all drones operating in the U.S. airspace to have remote ID capability to address safety, national security, and law enforcement concerns. Drones flying in FAA-Recognized Identification Areas (FRIA) may be partially exempt from this rule. Additionally, operators can fly drones in Class G (uncontrolled) airspace without air traffic control authorization, but operations in any other airspace need air traffic approval.
One such technology that addresses the FAA’s concern for safety and also minimizes risks of other aircraft, people and property is GhostWave Inc.’s integrated optical-radar sensor fusion system that utilizes radio frequency noise technology to generate millions of signals and read return signals at various range gates and, thus, helps pilots identify and classify non-cooperative threats in the flight path and avoid collision. The radars were patented by The Ohio State University and are exclusively licensed to GhostWave Inc.
The technology was funded by the Ohio Department of Higher Education-sponsored Ohio Federal Research Network, which is managed by Parallax Advanced Research, as part of the Sustaining Ohio’s Aeronautical Readiness and Innovation in the Next Generation (SOARING) Initiative. SOARING leverages state funding and Ohio’s unique aerospace assets to assist awardees, such as GhostWave Inc., in overcoming critical technical barriers and business challenges when innovating unmanned aerial systems (UAS), personal air vehicles (PAVs), unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), heavy-lift logistics delivery vehicles (LDAVs) and electric vertical takeoff and landing vehicles (eVTOLs).
“We are proud that our technology is ahead of industry in providing an essential safety solution for drone pilots. We hope that our technology can lead to new collaborations and business opportunities and ensure the safety of drone use for all operators and non-operators,” said Dean Zody, CEO of GhostWave Inc.
Click here for details on the new FAA Remote ID rules, waivers and important dates and deadlines.
Disclaimer: This Parallax/OFRN article is for informational purposes only and not for the purpose of providing legal or regulatory advice or counsel. You should contact your attorney to obtain advice with respect to any issue or problem regarding these rules and regulations.
###
About Parallax Advanced Research
Parallax is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit that tackles global challenges by accelerating innovation and developing technology and solutions through strategic partnerships with government, industry and academia across Ohio and the Nation. Together with academia, Parallax accelerates innovation that leads to new breakthroughs. Together with government, Parallax tackles critical global challenges and delivers new solutions. Together with industry, Parallax develops groundbreaking ideas and speeds them to market.
About the OFRN
The OFRN has the mission to stimulate Ohio’s innovation economy by building statewide university/industry research collaborations that meet the requirements of Ohio’s federal laboratories, resulting in the creation of technologies that drive job growth for the State of Ohio. The OFRN is a program managed by Parallax Advanced Research and Ohio State.
About GhostWave Inc.
GhostWave Inc.’s patented radars utilize a pseudo-random radio frequency generator to solve interference and jamming problems presented by other radars. GhostWave Inc. products have applications in three areas: UASs, low altitude threat detection, and studying bees.